Gum Disease 101: What Are the Symptoms and How Do I Treat It?
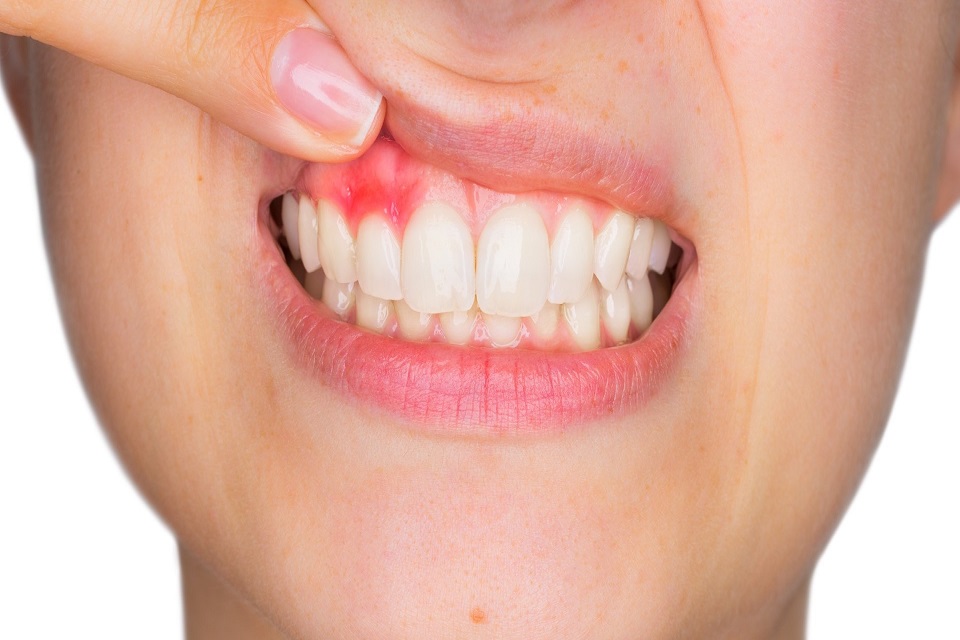
If you have red, tender, and swollen gums, then it’s likely that you have gum disease. That said, you might have the condition without displaying any of these symptoms.
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease refers to an oral health condition that affects the gums. In its mild form, it’s called gingivitis, while in its severe form, it’s called periodontitis. Both originate from bacterial infections.
When plaque and tartar accumulate around your teeth, they provide conducive conditions for the growth of bacteria. These bacteria attack your gums and make them bleed, a condition known as gingivitis. You can treat the symptoms through brushing and flossing regularly. However, if you don’t, gingivitis causes periodontitis.
Periodontitis weakens your gums such that they pull away from your teeth. As a result, plaque collects in the gaps between your teeth and if left unattended, it attacks your bone and gums and might cause tooth loss.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Most of the symptoms of gum disease take time to start showing. This means that you might have the condition without knowing.
Below are some of the symptoms of gum disease:
- Swollen, red, and painful gums.
- Bleeding gums when you brush your teeth or chew hard foods.
- Loose and misaligned teeth.
- Loosely fitting dentures.
- Persistent bad breath, even after brushing.
- Mouth sores and signs of infection, such as pus.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Here are some practices you need to observe to maintain healthy gums.
Get Regular Checkups
Regardless of your age, it’s crucial to get regular dental checkups. Older people should visit the dentist more often as they are vulnerable to gum disease.
Ideally, it would be best if you visited a dentist once every six months. They will clean your teeth, remove plaque and check for any complications before they worsen.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking weakens your immune system. As a result, mouth sores take longer to heal, increasing the risk of gum disease. If you don’t smoke, don’t start, and if you do, try quitting before it hurts your health.
Observe Dental Hygiene
As mentioned earlier, plaque and tartar increase the risk of contracting gum disease. For this reason, it’s wise to observe dental hygiene. Ensure that you brush your teeth at least twice daily, especially before you sleep. Also, floss daily to remove the food particles stuck between your teeth. It’s also good to drink a lot of water after every meal.
How to Treat Gum Disease
Here are the methods used for treating gingivitis before it progresses into periodontitis.
Professional Dental Cleaning
Professional dental cleaning involves two processes – scaling and root planning. Scaling gets rid of bacteria, plaque, and tartar from the surface of your teeth and around your gums.
On the other hand, root planning removes bacteria, prevents the build-up of tartar, smooths root surfaces, and facilitates proper healing. Here, the dentist uses lasers and ultrasonic equipment to clean your teeth.
Dental Restoration
It isn’t easy to clean your teeth if they are misaligned or when you have loose dentures. These restorations can also irritate your gums and cause gum disease. If this is the case, your dentist will fix these problems before prescribing other medication.
Ongoing Care
After several cleaning sessions, gingivitis goes away. However, you’ll need to keep good oral hygiene if you don’t want the condition to recur. Your dentist will create a plan and recommend the best practices for healthy teeth and gums.
Wrapping up
Gum disease tops the charts in oral diseases. Yet, surprisingly, most of its victims don’t know that they have it. Over time gum disease increases the risk of heart disease, some cancers, stroke and might cause tooth loss. Before it worsens, it’s crucial to visit a dentist and observe oral hygiene.




Pingback: 6 Signs You Might Need Dentures